Wood: The Building Material of the Future – Leading the Way for Tomorrow’s Natural Constructions

Wood is not just a material of the past; it is the material of the future. Wood is poised to redefine the construction landscape, creating healthier and sustainable living spaces, for generations to come. Discover insights and forecasts for global wood production, exploring trends, market dynamics, and the role of wood in the sustainable construction materials development.
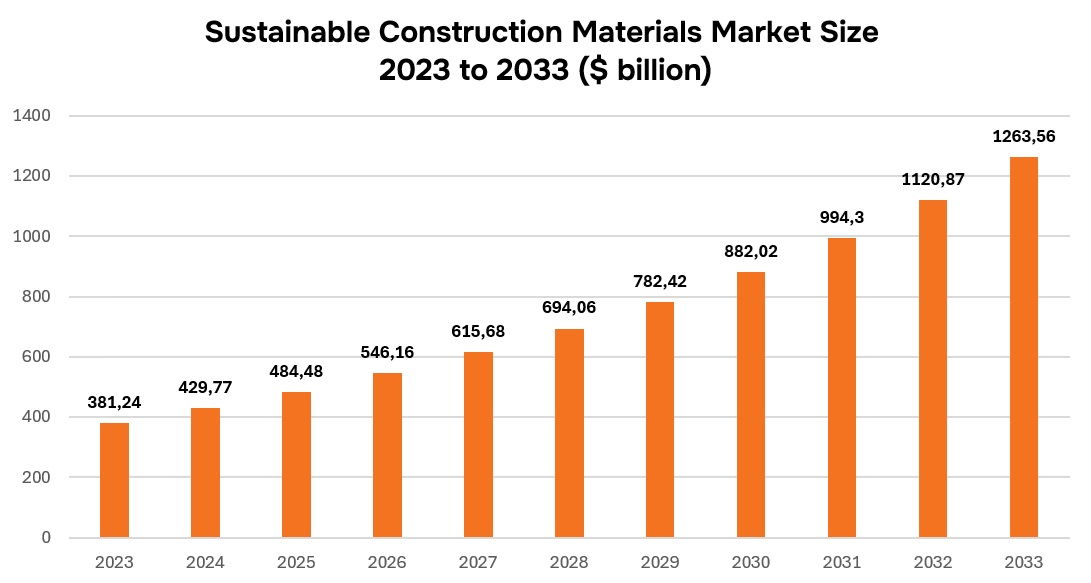
- Sustainable Construction Materials - impressive market CADR of 12.73% over 2023-2033!
- The Environmental Edge of Wood
- Innovations in Wood Construction
- Sustainability and Circular Economy
- Health and Well-being Benefits
- Economic Opportunities
- Versatility in Construction and the Market
- Challenges and Mitigation
- A Boon for Technological Solutions in Wood Processing - Automation and Digitization
- A Vision for the Future... all in Wood
- Sources
- About the Author
Sustainable Construction Materials - impressive market CADR of 12.73% over 2023-2033!
Wood plays a vital role in the rapidly expanding sustainable construction materials market, blending its natural advantages with cutting-edge innovations to meet growing global demand. As a renewable, carbon-storing resource, wood aligns perfectly with the principles of green building and environmental stewardship.
The global sustainable construction materials market is poised for significant growth, with its size increasing from USD 381.24 billion in 2023 to a projected USD 1,263.56 billion by 2033, at an impressive CAGR of 12.73% over the forecast period. Key trends driving this market include:
- Rising Demand for Green Buildings: Increased awareness of environmental issues and a shift toward sustainability are boosting demand for eco-friendly construction materials.
- Emergence of Advanced Materials: Innovations in material science, manufacturing techniques, and automation are creating cost-effective, high-performance sustainable materials.
- Learning and Development Initiatives: Programs like CEMEX UK’s Sustainable Construction Academy are educating industry professionals on integrating lower-carbon materials into projects.
- Bamboo’s Dominance: Bamboo, a fast-growing and renewable material, leads the market due to its versatility and environmental benefits, being used for flooring, wall panels, and structural components.
- Industrial and Residential Sectors: The industrial segment leads in adoption due to strict sustainability regulations, while the residential segment is growing rapidly as consumers and governments prioritize eco-friendly housing.
Challenges such as high production costs remain, but long-term savings, regulatory incentives, and growing consumer demand are set to drive the market forward.
The predictions for the sustainable construction materials market highlight several innovative and eco-friendly materials that are poised to shape the future of construction. Key materials include:
- Bamboo: A rapidly renewable resource known for its strength, flexibility, and minimal environmental footprint.
- Reclaimed Wood: Recycled timber from existing structures, reducing the demand for new lumber and helping to preserve forests.
- Green Insulation Materials: Insulating materials made from renewable or recycled sources, offering both thermal efficiency and lower environmental impact.
- Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): Pre-fabricated panels that provide excellent insulation and structural integrity, contributing to energy-efficient buildings.
- Cross-laminated Timber (CLT): A sustainable alternative to steel and concrete, offering strength, durability, and carbon storage.
- Recycled Metal: Metals such as steel and aluminum that are sourced from old materials, significantly reducing energy use and waste.
- Precast Concrete: Concrete elements that are manufactured off-site and then assembled, offering greater control over material waste and efficiency.
- Recycled Plastic-based Cement: A groundbreaking development that incorporates recycled plastics into cement production, lowering its carbon footprint.
- Others: Various other materials, such as eco-friendly paints and low-impact flooring, are also gaining traction.
These materials are increasingly in demand as construction sectors worldwide embrace sustainability and seek solutions that align with environmental and energy efficiency goals.
The Environmental Edge of Wood
Unlike concrete or steel, wood has a minimal environmental footprint. It is renewable, recyclable, and biodegradable, making it a cornerstone of a circular economy. Trees absorb carbon dioxide during their growth, and when used in construction, this carbon remains stored, reducing the overall carbon footprint of buildings. This positions wood as a climate-positive material, crucial in combating global warming. However, the challenge remains balancing the need to cut trees for production with ensuring sustainable forest management and minimizing environmental impact.

Innovations in Wood Construction
Advancements in engineered wood products, such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glued laminated timber (glulam), have revolutionized wood construction. These materials offer exceptional strength, fire resistance, and durability, rivaling traditional materials like concrete and steel. CLT, for instance, allows for the creation of prefabricated, large-scale components, enabling faster and more efficient construction while maintaining high precision.
Moreover, modular building systems using wood are gaining popularity. These systems emphasize prefabrication and standardization, reducing construction waste and labor costs. Wood’s adaptability allows for innovative designs, from skyscrapers to residential homes, demonstrating its versatility.
Sustainability and Circular Economy
Wood aligns with the principles of a circular economy through cascading use. This approach maximizes the lifecycle of wood products by reusing and recycling them across various applications, from primary structures to bioenergy at the end of their life. Poland, where forests cover over 30% of the land, has embraced this concept to sustain its forestry resources while supporting industries like furniture and construction.

Health and Well-being Benefits
Studies have shown that wooden environments positively affect mental and physical health. Wood in interiors improves air quality, regulates humidity, and provides a natural aesthetic that reduces stress and enhances well-being. This has prompted architects to increasingly incorporate wood into both residential and commercial spaces, capitalizing on its biophilic properties.
Economic Opportunities
The global shift toward sustainable materials has created significant economic opportunities. Wood-based construction supports job creation in forestry, manufacturing, and design sectors. It also positions nations like Poland, which has a robust wood industry, to become global leaders in sustainable construction solutions.
Poland’s wood processing industry is highly diverse, covering several key branches. These include sawmills, which produce sawn timber for construction and furniture; engineered wood products, such as plywood, MDF (medium-density fiberboard), and CLT (cross-laminated timber), essential for modern construction; and wooden components, including flooring, doors, windows, and decorative elements. Additionally, Poland excels in the production of furniture components and finished furniture, supported by world-class manufacturers that contribute to the global market.

Versatility in Construction and the Market
Wood’s influence extends far beyond primary structures to a wide array of essential construction and market materials. In construction, wood-based products are widely used in doors, windows, flooring, and interior paneling. Wooden windows and doors not only enhance energy efficiency but also offer superior thermal insulation, contributing to the energy performance of buildings. High-quality wood flooring, such as parquet or engineered hardwood, is favored for its durability, aesthetic appeal, and ability to be refurbished.
Furniture, a key segment of the wood-based market, showcases the material’s versatility. From classic solid wood designs to modern composite structures, wooden furniture enhances both functionality and style. Wood derivatives like medium-density fiberboard (MDF) and plywood are integral in producing affordable yet sturdy furniture and cabinetry.
Additionally, advancements in wood technology have broadened its application in other components like wooden insulation panels, which improve energy efficiency, and laminated veneers used in curved designs and structural elements. These innovations reinforce wood’s status as a sustainable and multifunctional material in both the construction industry and consumer markets
Challenges and Mitigation
While the global sustainable construction materials market is experiencing rapid growth, high production costs remain a significant restraint. Sustainable materials often involve advanced manufacturing processes, eco-friendly raw materials, and adherence to rigorous environmental standards, which collectively raise their production costs. This translates into higher market prices, making these materials less accessible for some builders and contractors. Additionally, competition with traditional, less expensive construction materials further challenges their market penetration.
The protection of forests remains a critical challenge despite the benefits of using wood. The demand for timber highlights the need for responsible forest resource management and a more sustainable supply chain. Key solutions involve adopting sustainable forestry practices, including certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), which ensure ethical sourcing. Additionally, robust policies that promote responsible harvesting and efficient timber processing are essential to balance economic needs with environmental conservation.
Despite all this, ongoing advancements in manufacturing efficiency and government incentives aimed at promoting sustainability are helping to mitigate the cost barrier and boost adoption.

A Boon for Technological Solutions in Wood Processing - Automation and Digitization
The rise of wood as the construction material of the future underscores the growing need for precision in processing and quality control. Companies like KSM Vision, which deliver advanced vision systems such as WoodSpect, are integral to this evolution. These systems detect defects in wood-based products, ensuring that raw materials meet the high-quality standards required for modern construction and furniture manufacturing.
By automating defect detection, KSM Vision helps optimize the use of wood, minimize waste, and enhance the efficiency of production lines. As the demand for wood-based products rises, innovations like automated machine vision system WoodSpect for quality control in wood processing will become increasingly vital for maintaining sustainability and competitiveness in the market.
A Vision for the Future... all in Wood
Wood is increasingly recognized as a key material for sustainable development in construction, blending environmental benefits, technological advancements, and economic opportunities. Its unique characteristics, coupled with new construction systems, make it a prime candidate for shaping the future of architecture and infrastructure.
Sources
https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sustainable-construction-materials-markethttps://biznes.meble.pl/edukacja/drewno-jest-surowcem-jutra/
About the Author
At KSM Vision, we are a trusted partner in automated quality control for major market players in industries such as: FMCG, pharmaceuticals, woodworking, building materials.
Combining AI deep learning algorithms with custom hardware, we create the most innovative quality control systems tailored to the individualized needs of a given high-volume manufacturer (for example, offering detection of a specific defect or process).
KSM Vision’s customized quality control solutions respond to corporate challenges. The flexibility of KSM Vision’s artificial intelligence-based optical vision systems enables: full integration with the company’s IT infrastructure, adaptation to any production infrastructure, meeting specific requirements and quality control processes, while handling high-volume production.
Production automation using vision systems based on deep neural networks (deep learning AI) makes it possible to eliminate manual quality control, increasing the profitability and scalability of production.
The innovation of KSM Vision’s systems is based on big data analysis and data mining algorithms, so our solutions not only automate production processes, but contribute to their optimization based on the analysis and statistics provided.
– Are you facing unresolved problems related to product defects?
– Are there processes in your factory where manual inspection is still used?
Find out how KSM Vision engineers can support your production facility: Contact us at KSM Vision

