The Growing Challenge of Mislabeling in FMCG: Data, Causes, Consequences, and… Solutions!

From ingredients and allergens to expiration dates, labels are integral to conveying essential information to consumers, ensuring product safety, and maintaining brand integrity. However, mislabeling incidents still poses a significant challenge for producers, especially global FMCG manufacturers exporting goods. With full containers or product lots still withdrawn from the market due to mislabeling the significance of correct labelling cannot be overpriced. Why is this problem even present in the era of automated quality control?
- Market statistics for product recalls due to mislabeling
- Global product rejections due to improper labelling Official data for: July 2024 alone
- EU product rejections due to improper labelling Data for: EU, Mid August-Mid September 2024 alone
- Causes of Mislabeling in the FMCG Sector
- Consequences of Mislabeling
- Automation and Digitization: A Solution to Mislabeling
- Data for market recalls due to mislabeling is still high - what hinders automated machine vision systems for label inspection?
- Inspect 360+ LI RS by KSM Vision: Ultimate Solution to Labelling Qaulity Control Automation
- Are you a corporate manufacturing plant representative and require more information or consulting?
In the global fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry, mislabeling remains a critical and complex issue. Ingredients or allergens missing on the label? Incorrect label language? Wrong expiry date? Labels are integral to conveying essential information to consumers, ensuring product safety, and maintaining brand integrity. How is that even possible that in the era of Artificial Intelligence, automation & robotics in the factories, the mislabeling issue is still present causing sginificant consequences for manufacturers, consumers, and the environment? Let’s dive deeper into the issue and explore the numbers.
Market statistics for product recalls due to mislabeling
Recent data on label quality control reveals alarming statistics related to mislabeling. Accurate labeling is crucial not only for consumer trust but also for legal compliance, as mislabeling can pose serious health risks. In the food industry alone, approximately 40% of product rejections in regions like the EU and USA are due to improper food labels, with 30% of recalls attributed to undeclared allergens. These figures underscore the immense challenge and urgency for manufacturers to maintain stringent labeling standards.
Here is some detailed market data on the product recalls due to labeling errors.
Sources:
IFS certification
European Commission
Global product rejections due to improper labelling Official data for: July 2024 alone
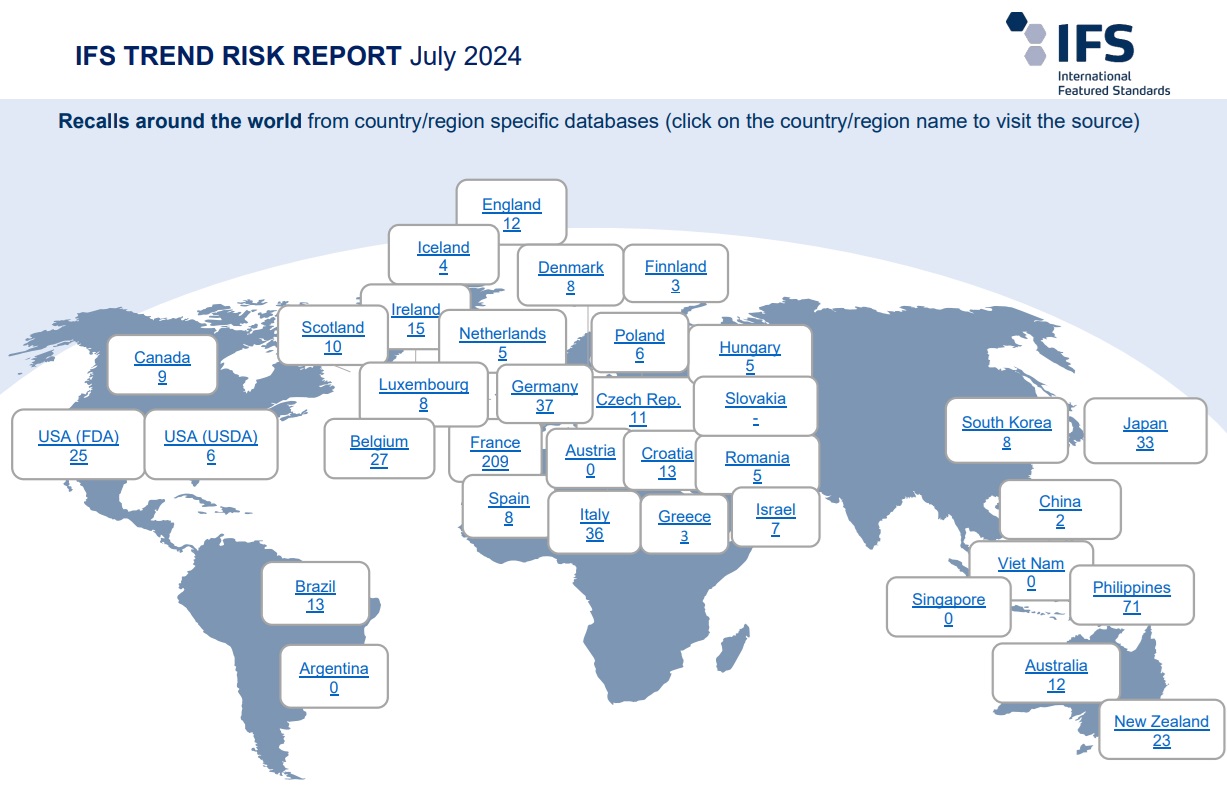
EU product rejections due to improper labelling Data for: EU, Mid August-Mid September 2024 alone
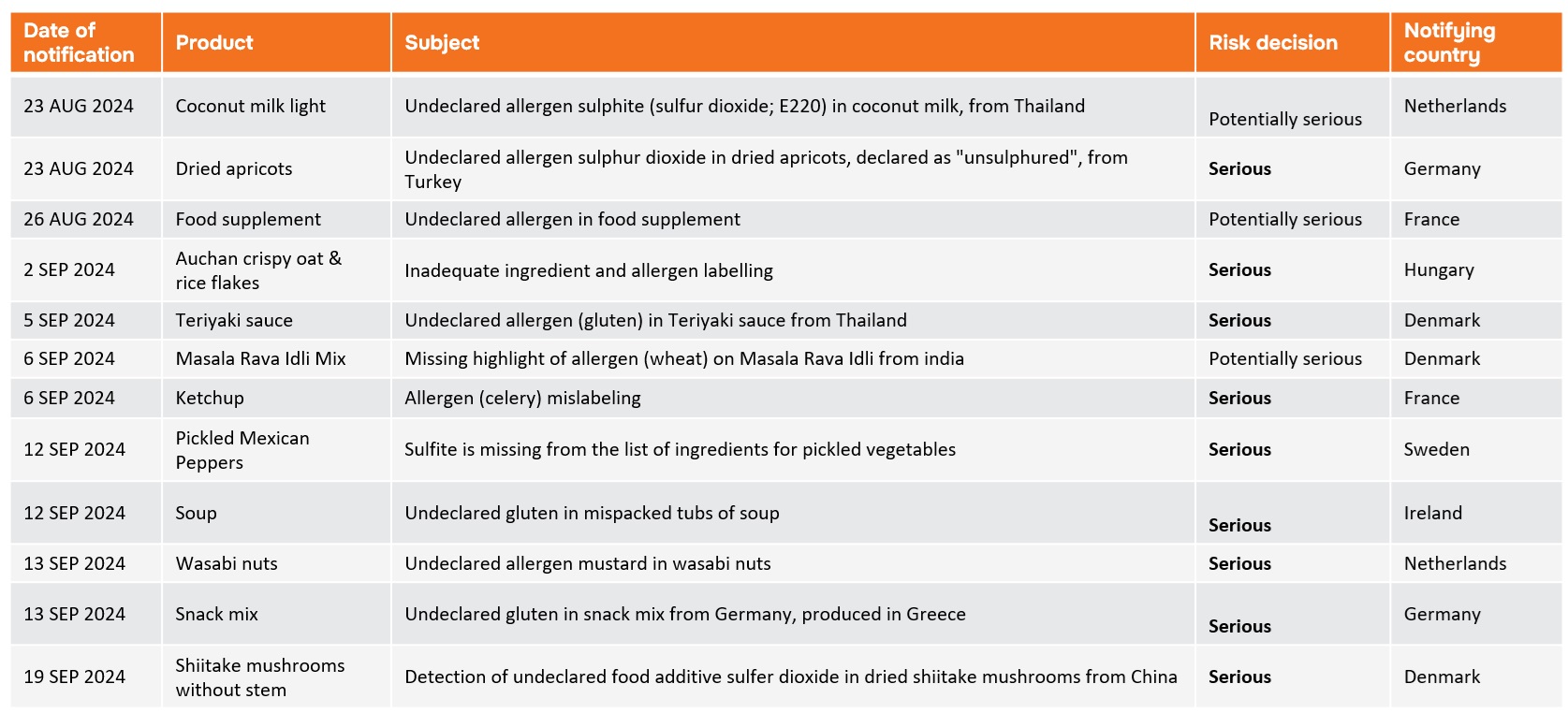
Causes of Mislabeling in the FMCG Sector
Mislabeling in FMCG products can result from several factors, including human error, inadequate quality control, supply chain complexity, and inefficient labeling processes. Here’s a closer look at each:
-
Human Error
Despite the increase in automated systems, many labeling tasks are still dependent on human labor. Currently quality control systems for packaging inspection are manually configured by operators directly on the production line, leading to human errors and potential downtimes. Human error in these processes can occur due to several factors, including fatigue, lack of training, or simple oversight. In the case of global FMCG producers exporting their goods to different markets with local legal requirements towards the product labelling, the label errors may occur easily and more often. When a worker assigns an incorrect label on a batch, the mistake may go undetected until the whole product lot is produced, container of products reaches the destination abroad, or – in worst case scenario – the product batch has already reached the consumer market, i.e. the maket shelf.
-
Complexity in Label Requirements
The FMCG industry faces intricate labeling requirements, especially in the case of production of products like food, beverage, cosmetics, chemistry or pharmaceuticals. These regulations vary by region and often change based on new scientific findings or regulatory mandates. Manufacturers may struggle to keep up with these requirements, resulting in unintended mislabeling. The complexity increases with international distribution, as products require localized labeling to meet country-specific regulations.
-
Supply Chain Complexity and Communication Gaps
Modern supply chains are vast and involve multiple stakeholders, from raw material suppliers to packaging providers and distribution networks. Communication gaps within this complex network can result in incorrect labeling information being used. For instance, if an ingredient supplier changes the composition of a raw material but fails to notify the manufacturer promptly, the final label may not reflect the correct ingredients, posing risks for allergen labeling and consumer safety.
Rapid production cycles often pressure high-volume manufacturers to move products quickly down the line. However, this pressure can lead to rushed processes and errors. Labels may be incorrectly applied or printed inaccurately during these high-speed operations. Moreover, outdated equipment or a lack of synchronized systems across production lines can increase the risk of mislabeling.

Consequences of Mislabeling
Mislabeling has far-reaching consequences that affect not only the manufacturers but also consumers, regulatory authorities, and the environment.
-
Financial and Operational Losses and Product Recalls
For FMCG manufacturers, mislabeling can result in substantial financial losses and operational… nightmare. The costs associated with recalling mislabeled products from the market include logistics expenses, product disposal fees, and compensation for retailers. A large-scale recall often involves removing entire lots or containers from multiple retail locations, leading to millions of dollars in losses. Additionally, these recalls disrupt supply chains, affecting the delivery timelines and relationships with suppliers and retailers.
-
Hindered Sustainability Goals and Environmental Impact
Mislabeling often results in entire containers or lots being removed from the market and disposed of, even if the products themselves are safe for consumption or use. This leads to a massive waste of resources, including packaging materials, labels, and the products themselves. When food items are involved, mislabeling contributes to food waste, exacerbating the global food security crisis. Furthermore, the disposal of these products contributes to landfill accumulation and increased carbon emissions. Hence, mislabeling due to manual errors related lead to potential downtimes, hinder automation and digitization goals, and affect adherence to zero-waste and eco-friendly regulations.
-
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
Mislabeling can result in legal actions and regulatory fines. In regions like the European Union and the United States, strict labeling laws mandate full disclosure of ingredients, allergens, and accurate descriptions of products. Regulatory bodies often impose fines on manufacturers for non-compliance with these standards. In some cases, severe violations can lead to bans or restrictions on the sale of products, especially if multiple mislabeling instances occur.
-
Consumer Health Risks
Mislabeling poses a direct health risk to consumers, particularly in cases involving incorrect allergen information, nutritional content, or expiration dates – this occurs in particular for the food processing, beverage production including alcohol, pharmaceutical producs and cosmetics). For individuals with food allergies, consuming a product with undisclosed allergens can have severe or even fatal consequences. Inaccurate expiration dates may lead to the consumption of spoiled food, which poses health risks, while incorrect dosage information on pharmaceutical products can lead to overdoses or ineffective treatment.

Automation and Digitization: A Solution to Mislabeling
As mislabeling becomes a growing challenge, many manufacturers are turning to automation and digitization to enhance labeling accuracy and reduce human error. Machine vision systems, in particular, offer a powerful solution for quality control and can significantly improve labeling accuracy in high-speed production environments.
How does automated machine vision work?
Machine vision systems for labeling quality control work by using high-resolution industrial cameras, advanced software, and AI algorithms to inspect product labels in real time as they move down the production line. By capturing high-resolution images of labels and comparing them to reference templates, these systems can identify even the smallest inconsistencies, such as incorrect text, missing elements, or alignment errors. Machine vision technology can also scan barcodes, QR codes, and other identifying markers to ensure that the correct label is applied to each product.
Once an error is identified, the system can immediately flag the defective product, often diverting it from the production line before it reaches packaging or shipment stages. These systems can be configured to inspect a high volume of products at incredible speeds, making them highly efficient for large-scale manufacturing environments. Vision systems also track data from each inspection, which can be used to identify recurring issues or patterns, allowing manufacturers to make process adjustments to reduce labeling errors over time. By automating quality control, vision systems significantly reduce the reliance on human inspectors, lowering the chance of human error and enhancing overall labeling accuracy.
Any real-life example?
The example of vision inspection system for automated quality control of labels is Inspect 360+ LI by KSM Vision
The flexibility of Inspect 360+ LI allows you to apply the system for diverse formats:
- packaging – atomizer bottles, cartons, pouches, bags, doypacks, instant bags, bigbags, trays, sachets, bottles with unusual shapes and bends
- labels – paper labels, foil sleeve labels
Inspect 360+ LI provides full automated detection of potential label defects, including inspection and analysis of:
- BATCH, EAN, UFI codes
- label presence
- position/location of the label on the package
- inverted or upside down label
- skewing label
- peeling off
- wrinkles
- multiple labels
- unclear printing, blurred graphics, etc.
For sachets, pouches, zipper bags, “instant” meals, etc. Inspect 360+ LI additionally performs seal inspection:
- blurring text
- product height
- tightness
- top/side seal
- cutout (e.g. pouch)
- deformations
- lack of continuity of the seal
- foreign matter (typically small fragments of packaged food)
Inspect 360+ LI is tailored to meet corporate requirements, in terms of manufacturing plant IT systems: data exchange, user rights management, reporting.

Data for market recalls due to mislabeling is still high - what hinders automated machine vision systems for label inspection?
The significance of proper labeling cannot be overstated in today’s FMCG market. And yet, the stats for product recalls are still high as per data presented higher in the article. What hinders dealing with the proper labelling?
-
High Initial Investment
On the one hand implementing machine vision systems and automated labeling solutions requires significant upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and employee training. Small to medium-sized manufacturers may find these costs prohibitive, though they stand to benefit substantially in the long term from the reduction in errors and operational efficiency.
This is why it is important to choose the machine vision producer – OEM – offering the systems with short ROI period. For the above-mentioned KSM Vision Vision Systems the Return in Investment period can be as short as 12 months.
-
Integration with Existing Systems
For major manufacturers willing to invest in the automation the obstacle may remain the integration with the existing production infrastructure. Many manufacturers rely on legacy systems that may not easily integrate with modern automation solutions. Integrating machine vision technology with existing production lines requires careful planning and may necessitate equipment upgrades. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability with other systems, such as ERP (enterprise resource planning) and inventory management software, is crucial for successful implementation.
The solution to this is choosing the automated machine vision based on flexible architecture of neural networks as such architecture enables adaptation of the system to the existing IT system or manufacturing infrastructure. How? See Customized Vision System fo Label Inspection for details.
-
Manual configuration of vision systems by operators
The crucial cause for limited performance of vision systems in regards to ensuring proper labelling is the fact that currectly the automated quality control systems for packaging inspection are manually configured by operators on the production line, letting for human errors. Current solutions on the market require manual handling, especially in terms of calibration and parameterization for new formats and products.
Any solution to the manufacturers’ challenges?
This production process challenge has not been tackled by any OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)… until now because KSM Vision has decided to design and develop such ‘100% automated and auto-calibrated label quality inspection system’ under the consortium with Campden BRI Hungary, and Maspex with the support of theEuropean Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT Food). The R&D project includes a process for automating and digitizing label quality testing to minimize production waste caused by errors on food product labels. The innovative label quality inspection system developed upon the R&D project will provide ‘100% automated product inspection on production lines’ thus simplifying the quality control procedure, resulting in reduction of FMCG waste -in this case with a focus on the food industry green transformation.

Inspect 360+ LI RS by KSM Vision: Ultimate Solution to Labelling Qaulity Control Automation
Inspect 360+ LI RS system offers fully automated machine vision for packaging label quality control. The system is dedicated for the global FMCG manufacturers who face mislabeling problems when exporting products.
Inspect 360+ LI RS label inspection system solves these issues with cutting-edge features unique in the quality control market, such as:
- Remote Setup of the system for the new label inspection by Marketing/Quality Assurance Department of the global FMCG manufacturer (not directly on the production line by the line operators)
- Double checking of the label content during remote setup by the business departments (before it is sent to factory for production)
- Auto-Calibration of the system based upon the remotely uploaded label artwork file.
Inspect 360+ LI RS is the 1st worldwide self-learning and auto-calibrated FMCG label vision inspection system generating strong added value for the high-volume manufacturing plants:
- Increased Operational Efficiency – Reduction of waste (in particular for manufacturers shipping to foreign markets), downtimes and manual labor.
- Automation & Innovative Edge – Leveraging automation and digitization to stay ahead in the market and scalability requirements
- Sustainability Goals Met – Minimizing waste, complying with regulations (in the event of a label fault, the entire product series can be withdrawn from FMCG market)
- Enhanced Product Quality – Customer safety and brand reputation.
Are you a corporate manufacturing plant representative and require more information or consulting?
At KSM Vision we specialize in advanced quality control and automation solutions that, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine vision technologies, effectively replace manual inspections, significantly improving both accuracy and cost-efficiency.
We offer a unique combination of machine learning algorithms with custom-designed hardware, fully integrated into existing production lines and IT systems (data exchange, permissions, reporting), ensuring smooth operations and full compatibility.
Our individualized approach allows us to tailor our solutions to meet the specific inspection needs and challenges of the plant/product, enabling us to effectively address corporate requirements.
This is a key differentiator for KSM Vision compared to other OEM manufacturers.
Are you facing unresolved issues with defects or any of your production processes still rely on manual inspection? You are most welcome to contact our engineers at welcome@ksmvision.com to share your production challenges. We will analyze your use-case, deliver as much know-how in the area of automation and machine vision (no matter the market supplier we will just advise the best solution in your particular case), and we will determine if KSM Vision’s customized solutions can address your challenges.

